Publications by Biognosys and Collaborators
Bekker-Jensen DB, Bernhardt OM, Hogrebe A, Martinez-Val A, Verbeke L, Gandhi T, Kelstrup CD, Reiter L, Olsen JV. Nature Communications
Protein phosphorylation is a predominant post-translational modification that dynamically regulates protein function and cell signaling. In this collaboration with the Olsen group at the University of Copenhagen, we showed that DIA allows reliable phosphosite localization for hundreds of samples and outperforms DDA in dynamic range, reproducibility, sensitivity, and accuracy. Additionally, directDIA, the library-free workflow of Spectronaut reaches phosphoproteome depths comparable to library-based DIA analysis.
Piazza I, Beaton N, Bruderer R, Knobloch T, Barbisan C, Chandat L, Sudau A, Siepe I, Rinner O, de Souza N, Picotti P, Reiter L. Nature Communications
Chemoproteomics enables protein target identification of bioactive compounds, unraveling the mode of action of drugs. In this joint effort with Prof. Picotti’s group, ETH Zurich, we presented a novel chemoproteomic workflow combining LiP and machine learning-based data analysis. This next-generation proteomics approach enables the identification of small molecule drug targets in complex proteomes and the analysis of their binding properties across species and drug target classes.
Salovska B, Zhu H, Gandhi T, Frank M, Li W, Rosenberger G, Wu C, Germain PL, Zhou H, Hodny Z, Reiter L, Liu Y. Molecular Systems Biology
In a collaboration between Prof. Liu’s group at Yale University and Biognosys, we established a combined DIA-MS and pulse SILAC approach to unravel the correlation between protein degradation and mRNA abundances in HeLa cells. Among other improvements, the direct pSILAC-DIA approach offers better quantitative accuracy and richer quantitative features if compared to alternative strategies, resulting in a correlation between mRNA level and protein degradation rates to be resolved at the isoform levels.
Revealing Dynamic Protein Acetylation across Subcellular Compartments
Baeza J, Lawton AJ, Fan J, Smallegan MJ, Lienert I, Gandhi T, Bernhardt OM, Reiter L, Denu JM. Journal of Proteome Research
In this study, the Biognosys’ R&D team, in collaboration with researchers of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, co-developed and benchmarked a DIA method to quantify acetylation stoichiometry in the cell proteome. This improved DIA method overcomes the limitations of DDA, allowing the accurate and reproducible quantification of light and heavy acetyl-lysine fragment ions. The method was benchmarked on synchronized cell lines with defined acetylation stoichiometry, providing a detailed landscape of the site-specific acetylation dynamics across cellular compartments.
Systematic Comparison of Strategies for the Enrichment of Lysosomes by Data Independent Acquisition
Singh J, Kaade E, Muntel J, Bruderer R, Reiter L, Thelen M, Winter D. Journal of Proteome Research
The lysosome is a critical cell compartment dedicated to the recycling of macromolecules and organelles, and it is associated with rare inherited fatal disorders. The analysis of lysosomal proteins by DIA requires a protocol for the enrichment of the lysosome fraction in a sample. In collaboration with the Winter lab at the University of Bonn, we achieved a high number of protein identifications and quantitative reproducibility by means of nanoparticle- and immunoprecipitation-based enrichment strategies.
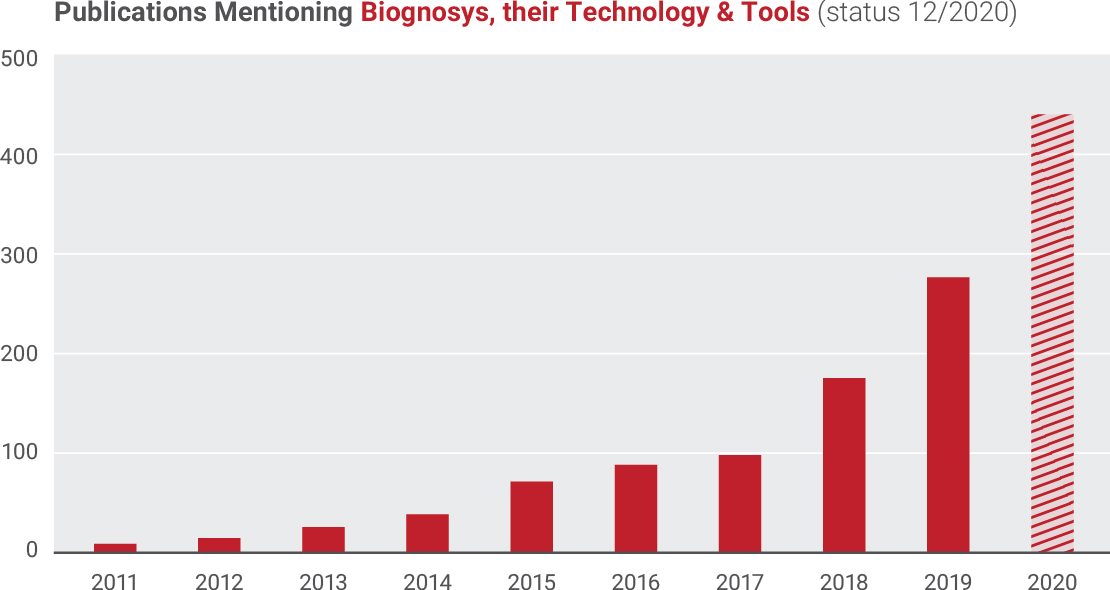
Publications Mentioning Biognosys, their Technology & Tools
Region-Specific Proteome Changes of the Intestinal Epithelium during Aging and Dietary Restriction
Gebert N, Cheng CW, Kirkpatrick JM, Di Fraia D, Yun J, Schädel P, Pace S, Garside GB, Werz O, Rudolph KL, Jasper H, Yilmaz ÖH, Ori A. Cell Reports
Changes in the intestinal epithelium caused by aging impair the normal absorption of nutrients, reduce gut barrier function, and increase the risk of disease. Researcher Dr. Gebert and coworkers measured region-specific proteome changes in the small intestine of mice by DIA and PRM and used Biognosys’ software Spectronaut and SpectroDive for data analysis. The authors showed how dietary interventions modulating ketone body signaling can partially restore a youthful crypt composition in the gut of old mice.
Proteome Profiling in Cerebrospinal Fluid Reveals Novel Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease
Bader JM, Geyer PE, Müller JB, Strauss MT, Koch M, Leypoldt F, Koertvelyessy P, Bittner D, Schipke CG, Incesoy EI, Peters O, Deigendesch N, Simons M, Jensen MK, Zetterberg H, Mann M. Molecular Systems Biology
The analysis of biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid is an important tool in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease before the onset of memory loss. A team of scientists led by Prof. Matthias Mann performed a multiple-cohort proteomics study to identify novel biomarkers for dementia. The authors employed SpectroMine to generate a Hybrid Library and Spectronaut for targeted DIA data extraction. Besides the usual candidates such as tau, the study showed a 40-protein signature of Alzheimer’s disease.
Rescue of Oxytocin Response and Social Behaviour in a Mouse Model of Autism
Hörnberg H, Pérez-Garci E, Schreiner D, Hatstatt-Burklé L, Magara F, Baudouin S, Matter A, Nacro K, Pecho-Vrieseling E, Scheiffele P. Nature
The oxytocin system is evolutionarily conserved, has important functions in the control of social behaviors, and has been implicated in the context of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). In this work, Dr. Hörnberg and colleagues used tandem mass tags (TMT) proteomics to unravel molecular alterations of the oxytocin signaling in dopaminergic neurons, and suggest that pharmacological interventions targeting such core processes may restore molecular signaling and benefit a wide range of patients with ASD.
The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Bouhaddou M, Memon D, Meyer B, White KM, Rezelj VV, Correa Marrero M, Polacco BJ, Melnyk JE, Ulferts S, Kaake RM, Batra J, Richards AL, Stevenson E, Gordon DE, Rojc A, Obernier K, Fabius JM, Soucheray M, Miorin L, Moreno E, Koh C, Tran QD, Hardy A, Robinot R, Vallet T, Nilsson-Payant BE, Hernandez-Armenta C, Dunham A, Weigang S, Knerr J, Modak M, Quintero D, Zhou Y, Dugourd A, Valdeolivas A, Patil T, Li Q, Hüttenhain R, Cakir M, Muralidharan M, Kim M, Jang G, Tutuncuoglu B, Hiatt J, Guo JZ, Xu J, Bouhaddou S, Mathy CJP, Gaulton A, Manners EJ, Félix E, Shi Y, Goff M, Lim JK, McBride T, O’Neal MC, Cai Y, Chang JCJ, Broadhurst DJ, Klippsten S, De Wit E, Leach AR, Kortemme T, Shoichet B, Ott M, Saez-Rodriguez J, tenOever BR, Mullins RD, Fischer ER, Kochs G, Grosse R, García-Sastre A, Vignuzzi M, Johnson JR, Shokat KM, Swaney DL, Beltrao P, Krogan NJ. Cell
This publication is an important joint effort of the scientific community to provide a quantitative mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics survey of SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The study showed that SARS-CoV-2 infection causes a dramatic rewiring of host and viral protein phosphorylation, stimulates filopodial protrusions, and induces cell cycle arrest. Finally, the authors identified potential antiviral drugs using a panel of kinase inhibitors.
Classification of Mouse B Cell Types Using Surfaceome Proteotype Maps
van Oostrum M, Müller M, Klein F, Bruderer R, Zhang H, Pedrioli PGA, Reiter L, Tsapogas P, Rolink A, Wollscheid B. Nature Communications
Molecular Classification of the Placebo Effect in Nausea
Meissner K, Lutter D, von Toerne C, Haile A, Woods SC, Hoffmann V, Ohmayer U, Hauck SM, Tschoep MH. PLoS One
Spatially and Cell-type Resolved Quantitative Proteomic Atlas of Healthy Human Skin
Dyring-Andersen B, Løvendorf MB, Coscia F, Santos A, Møller LBP, Colaço AR, Niu L, Bzorek M, Doll S, Andersen JL, Clark RA, Skov L, Teunissen MBM, Mann M. Nature Communications
A Streamlined Mass Spectrometry–based Proteomics Workflow for Large‐scale FFPE Tissue Analysis
Coscia F, Doll S, Bech JM, Schweizer L, Mund A, Lengyel E, Lindebjerg J, Madsen GI, Moreira JM, Mann M. Journal of Pathology
Immune Suppression in the Early Stage of COVID-19 Disease
Tian W, Zhang N, Jin R, Feng Y, Wang S, Gao S, Gao R, Wu G, Tian D, Tan W, Chen Y, Gao GF, Wong CCL. Nature Communications
Global and Site-Specific Effect of Phosphorylation on Protein Turnover
Wu C, Ba Q, Lu D, Li W, Salovska B, Hou P, Mueller T, Rosenberger G, Gao E, Di Y, Zhou H, Fornasiero EF, Liu Y. Developmental Cell
Karayel Ö, Xu P, Bludau I, Velan Bhoopalan S, Yao Y, Ana Rita FC, Santos A, Schulman BA, Alpi AF, Weiss MJ, Mann M. Molecular Systems Biology
Xuan Y, Bateman NW, Gallien S, Goetze S, Zhou Y, Navarro P, Hu M, Parikh N, Hood BL, Conrads KA, Loosse C, Kitata RB, Piersma SR, Chiasserini D, Zhu H, Hou G, Tahir M, Macklin A, Khoo A, Sun X, Crossett B, Sickmann A, Chen YJ, Jimenez CR, Zhou H, Liu S, Larsen MR, Kislinger T, Chen Z, Parker BL, Cordwell SJ, Wollscheid B, Conrads TP. Nature Communications
ELAV and FNE Determine Neuronal Transcript Signatures through EXon-Activated Rescue
Carrasco J, Rauer M, Hummel B, Grzejda D, Alfonso-Gonzalez C, Lee Y, Wang Q, Puchalska M, Mittler G, Hilgers V. Molecular Cell
Karayel O, Michaelis AC, Mann M, Schulman BA, Langlois CR. PNAS